Why do digital twins attract business, and why do manufacturing companies try to keep up with the times by investing considerable sums in this promising technology? Let's move forward to understand what digital twins are, why there are essential in manufacturing, and how to implement them.
What are Digital Twins, actually?
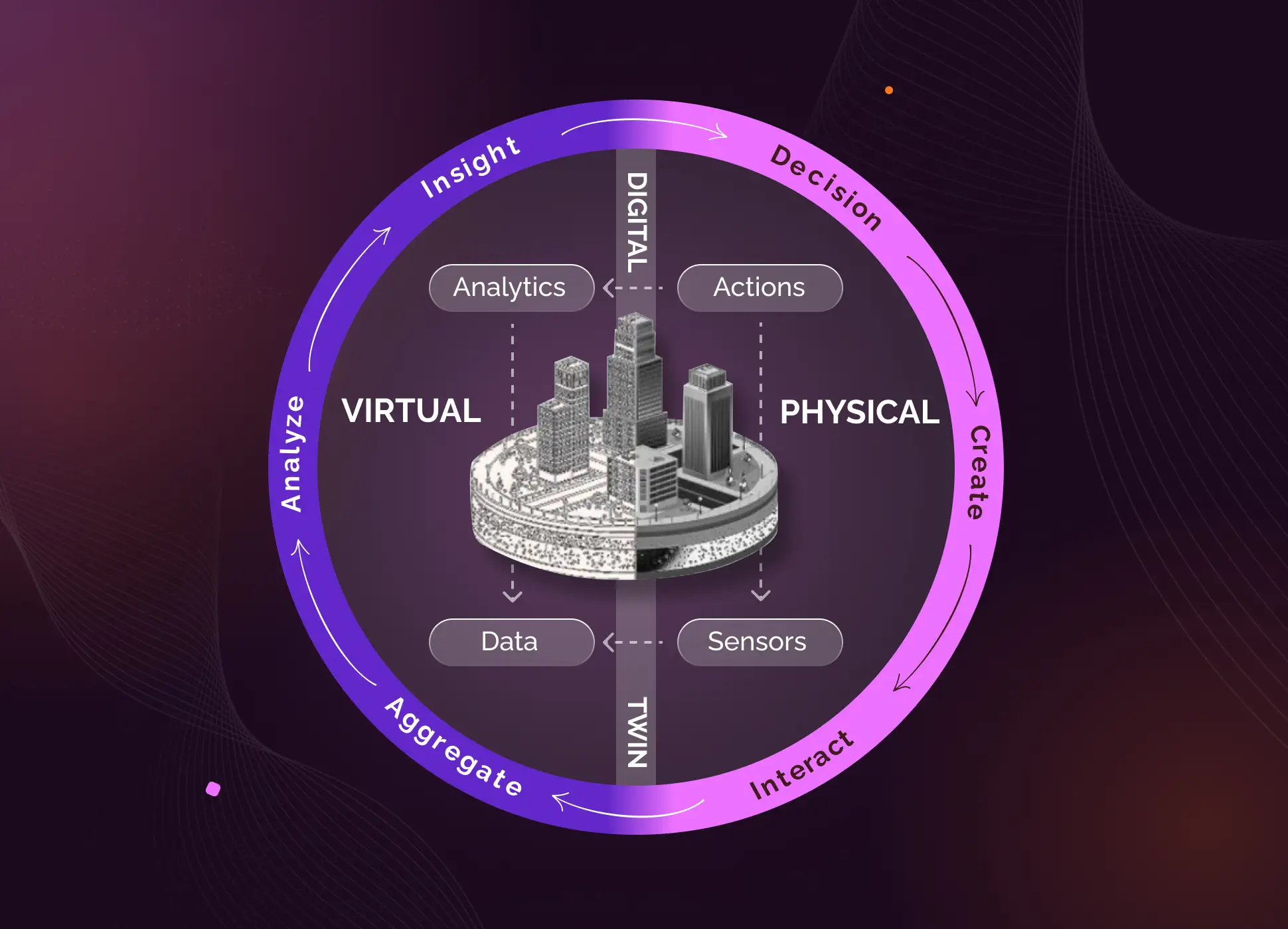
Digital twins are virtual models of objects, systems, or processes. They accurately reproduce the shape and actions of the original one and synchronize with them.
Digital twins are needed to simulate what will happen to the original object in one or another environment. They help, first, save time and money with complex and expensive equipment, and second, avoid harm to people and the environment.
The concept of digital twins was first described in 2002 by Dr. Michael Grieves, a professor at the University of Michigan. According to Grieves, "In ideal conditions, all the information that can be obtained from the physical product can be obtained from its digital twin".
Why Digital Twins are so Important in Manufacturing
Safety instructions, quality control, and assurance measures made possible by digital twins have significantly reduced the number of errors and accidents in the construction industry. Maintenance and operation using digital twins optimizes operations, reduces downtime, and lowers maintenance and staff costs.
Using digital twins has improved collaboration and communication in system design, facilitating data collection and cooperation coordination before construction.
But let's dig deeper and thoroughly review the pros of digital twins in manufacturing.
Pros #1 Increase Production Efficiency
There is one thing for sure, thanks to digital twins technology, collecting real-time data on equipment, tools, system performance, and employees opens up opportunities for improving production lines and conducting tests on digital models without risking the facility's performance.
Digital twins can monitor the entire manufacturing cycle from creation to the final product. Deploying digital twins made it possible to build reproductions based on historical performance data and use predictive reproduction results to plan future manufacturing process improvements. And improving performance leads to increased production speed and efficiency.
Pros #2 Enable Predictive Maintenance
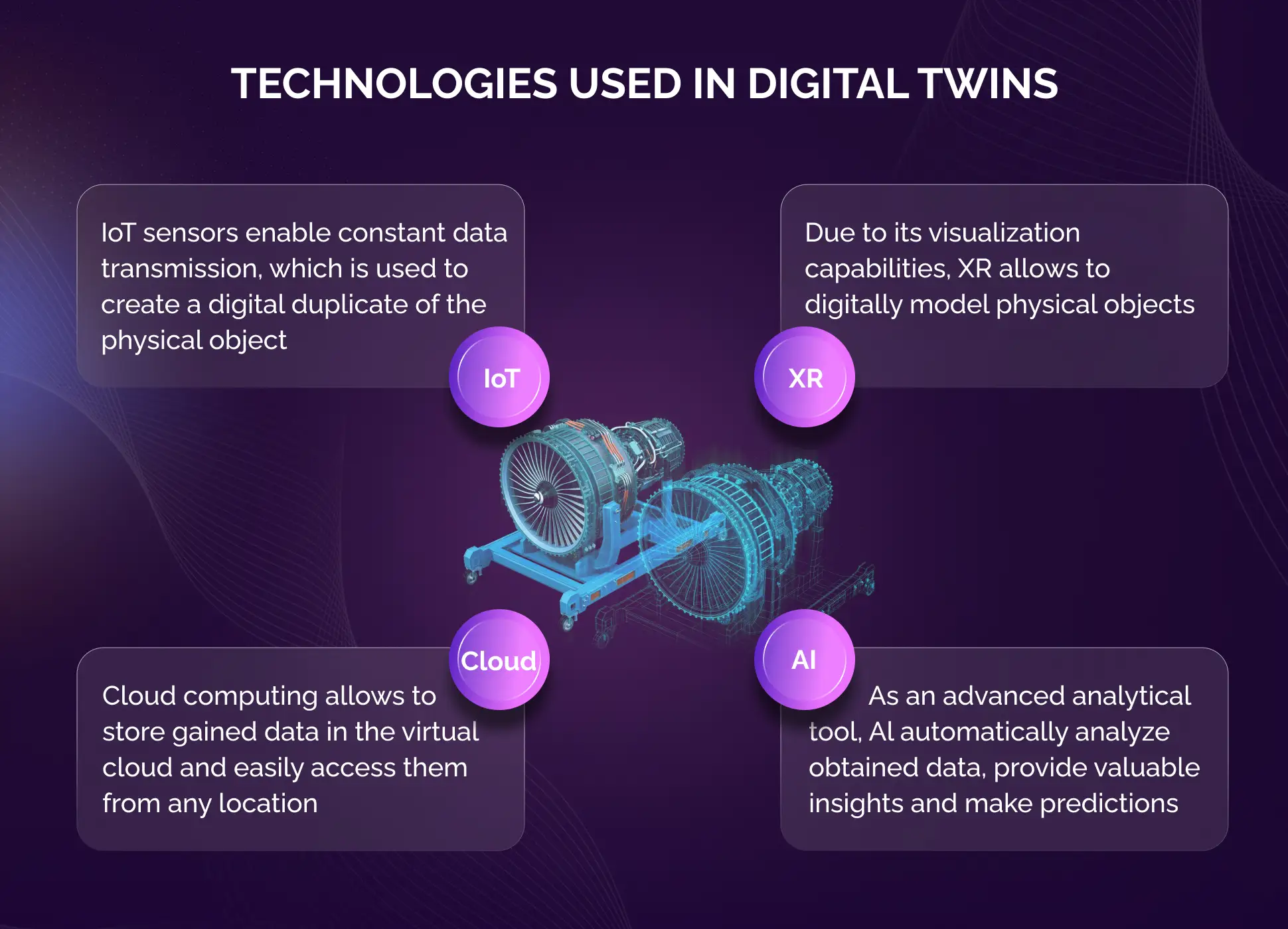
Digital twins are complex construction, and different technologies like IoT sensors, 3D CAD files, and AR (augmented reality) visualization are used to create a product of an ecosystem of real-time data transfer. With all this constant visibility and measuring, a concept like predictive maintenance becomes possible and practical.
Sensors regularly monitor the equipment by recognizing and evaluating each operation phase. This incident is recorded when there is a risk of component breakdown. Suppose this repeatedly happens across one or more devices. In that case, patterns emerge, which allows the digital twin to predict when and where the following breakdown will occur with incredible accuracy.
Pros #3 Preventing Injuries
How do digital twins ensure injury prevention, you may ask? First, let's see what the common injury causes in the manufacturing industry are.
- Proximity to faulty systems may cause hearing or vision damage.
- Muscle or tendon strain when lifting too heavy components.
- Fall injuries caused by climbing stairs and injuries from cuts.
- Splashing or temperature-related damages when pieces under pressure are dismantled.
Reducing such risk factors can be reduced by managing digital twins and their entire virtual environment, giving professionals more confidence and knowledge about what to expect during real work.
Another way how digital twins can measure compliance is to track workers' proximity to machines and dangerous areas. The wearable tracking sensors help companies track their employees' movement around the production site and send warnings when a digital site tags someone's security.
Pros #4 Product Testing and Reducing Time to Market
Creating new or updated products requires long periods of trial and error in the manufacturing model. With digital twins, you can design and test in simulation using various scenarios and do it quickly and at a lower cost, which may lead to better and more timely products.
Moreover, digital twins accurately replicate test activity and can predict future states to determine equipment or product malfunctions. In addition, the digital twins will ensure the repeatability and reliability of the test actions thanks to a better understanding of the system's sensitivity.
One of the key ways to reduce labor time and costs during manufacturing is the digitization of equipment monitoring processes. When anomalies are detected in the digital twin, maintenance specialists may be involved instead of regular scheduled monitoring and maintenance. It can also prevent production outages related to routine monitoring and maintenance and reach the market on time.
What is Digital Twins Software Used by Companies?
Here, we have learned that thanks to digital twins, manufacturing industries can easily design and optimize systems, carry out preventive maintenance, and optimize industrial asset management.
Also, digital doubles will allow you to analyze the results of preventative maintenance in order to save on warranty and insurance costs and optimize the operation of your product. And what software is used by companies to design digital twins? Let's move forward to learn the three best software programs and platforms for modeling digital twins and study a few case studies.
Omniverse Enterprise by NVIDIA is a scalable, end-to-end platform for building and operating metaverse applications. It is based on Universal Scene Description (USD), which allows companies to connect and customize complex 3D pipelines and manage extensive, physically accurate virtual worlds.
From conceptual design for animated films to industrial digital counterparts of factories, Omniverse Enterprise is changing its approach to creating and using metaverse applications for architecture, design, construction and operation, media and entertainment, and manufacturing industries.
ANSYS Twin Builder enables the implementation of complete virtual prototypes from real systems. It combines the power of a multi-domain system modeling tool with extensive libraries for specific 0D applications, three-dimensional physics solvers, and reduced-order model (ROM) capabilities. Combined with the built-in software development tools, Twin Builder allows you to reuse existing components and quickly create a system model of your product.
By implementing ANSYS Twin Builder, you can increase net profit, manage expenses, and keep a competitive advantage. For example, digital twins will allow you to analyze the results of preventive maintenance to save on warranty and insurance costs and optimize the operation of your product.
Siemens NX is a universal and powerful integrated solution for delivering higher-quality goods faster and more efficiently. Companies can realize the advantages of digital twins with the help of NX, which provides next-generation solutions for designing, simulation, and manufacturing products.
NX provides a comprehensive set of tools that integrates disciplines, protects data integrity and project intent, and simplifies the process by supporting every product development phase, from conceptual design to modeling and production.
Engineers can use the generative design method to create new elements faster while respecting design constraints. This approach is iterative and gives quick results. It helps engineers make necessary adjustments by changing conditions to focus on the optimal design that meets the requirements.
Digital Twins Case Study #1: Mercedes Turns to Next-Generation Factories with Nvidia Omniverse
Car manufacturer giant Mercedes Benz uses Omniverse by Nvidia to design, plan and enhance its manufacturing and assembly facilities. Thanks to Omniverse, a car manufacturer develops a factory's digital twin and simulates new production processes without disrupting existing automotive production. Nvidia says that having a virtual workflow will allow Mercedes to respond quickly to supply chain disruptions and reconfigure the assembly line as needed.
A complete factory simulation can help the automaker pinpoint possible blockages, establish more ergonomic working conditions, or analyze where a robot cannot complete a task before production starts.
Digital Twins Case Study #2: Atomberg uses Ansys Simulation Solutions to Reduce its Buyers' Energy Consumption by 65%
The Atomberg team used Ansys software to form a more compact and energy-efficient design of a brushless DC motor, allowing approximately three Atomberg fans to use the same power required by one fan based on an asynchronous motor. It means it consumes 28 watts of electricity, compared to the 70-80 watts necessary for a conventional asynchronous motor. Can you imagine that? As a result, we have a more innovative and integrated (IoT)-enabled ceiling fan that consumes 65% less electricity than ordinary fans.
Digital Twins Case Study #3: Siemens NX Empowers Building Information Modeling (BIM) with the Digital Twins
Many solutions and software are used for specific workflows in the BIM industry. Still, not all of them integrate and work together. Since the building has fire sensors, plumbing for fire extinguishing, and determining whether doors are open or closed, all these should be connected. It is logical for the tools used for their construction and design to be connected as well. However, this problem has only been highlighted in the last six months since it creates a lack of performance and the ability to simulate the collaboration of building properties and functions. Siemens NX and its digital twin solution solve this problem.
Max Bogl, a construction company from Germany, decided to have more integrated tools, as their designs were too complex for the solutions they used. Starting with NX for Manufacturing, they began using other Siemens Digital Industries Software solutions to create a comprehensive digital twin and thread. Integration products such as NX for Design, NX for Manufacturing, and Teamcenter make the perfect BIM solution for construction companies.
How to Implement Digital Twins Technology
Today, creating a digital double has become much easier than before. There are even some predictions that digital twins will become the next feature of Internet of Things applications by 2026.
However, implementing a digital double into the structure may be challenging. The most important thing that enterprises will need to consider is how they will integrate the equipment and infrastructure while ensuring that the twin meets the individual needs of each department.
The first thing to do is learn the following step-by-step guide on implementing digital twin technology in an enterprise.
Meeting with Stakeholders
Involving all stakeholders in implementing and designing digital twins from the earliest stages is critical. Because regardless of the purpose of using the digital twin, every department or person who needs it may help developers of digital twins to consider any assets or goals they may miss out on. The participation of stakeholders will ensure that all use cases are considered.
Establishing data sources
A digital twin acts as an information center, tracking and collecting readings from various data sources. It is intentional because it allows end-users to analyze how different assets work together in ways that are difficult to achieve manually. The second important step is to establish sources based on the scale of your project. In order to determine precisely how many data sources are required, it is necessary to understand the number of assets incorporated into the digital twin.
Choosing the infrastructure
Though digital twins exist in digitized environments, they still need real-world infrastructure to work. Every asset requires a way to connect to the twins' network. Here IoT technology comes to play, making it far easier to integrate and manage devices effectively. The only thing that is required to implement them by humans. The following devices are required:
- Sensors are needed to collect data from the physical environment. What kind of sensor to choose depends on the digital twin's purpose. For example, motion sensors might be necessary for retail enterprises, but with a gas refinery - seismic monitors.
- A centralized platform is required to store all relevant information. Some enterprises prefer these platforms installed on physical servers. In contrast, others use off-site systems that generate visualizations in the cloud.
- The data transmission medium is needed to transmit data between the sensors, the centralized platform, and any devices users operate remotely. WiFi or Bluetooth is easy to implement, and sometimes Ethernet cables may be a practical solution.
Wrapping up
So what does all this mean? Digital twins are powerful tools for manufacturers to improve processes and predict future behaviors using machine learning. Establishing a digital twin can boost the productivity of almost any space, thanks to its combination of rapid real-time feedback and AI-powered predictive modeling.