1. The Big 3 Cloud Providers
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS, launched by Amazon in 2006, remains the undisputed leader in cloud services. Its extensive global infrastructure spans data centers across continents, ensuring low-latency access to services. AWS offers a comprehensive suite of services, including EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) for scalable virtual servers, S3 (Simple Storage Service) for object storage, and Lambda for serverless computing. Its dominance in the market is attributed to early adoption, a vast partner ecosystem, and a robust set of features.
Microsoft Azure
Azure, Microsoft's cloud platform, has rapidly gained ground since its launch in 2010. Leveraging Microsoft's enterprise expertise, Azure provides seamless integration with Windows-based systems and tools. Organizations already invested in Microsoft technologies find Azure appealing due to its compatibility with Active Directory, Office 365, and Windows Server. Azure's services cover everything from Azure Virtual Machines to Azure Cosmos DB and Azure Functions.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google's entry into the cloud market came later, but GCP has made significant strides. Known for its data-centric approach, GCP offers services like BigQuery for analytics, Compute Engine for virtual machines, and Kubernetes Engine for container orchestration. Google's expertise in machine learning and AI is evident through services like AutoML and TensorFlow. GCP's focus on innovation and simplicity appeals to developers seeking cutting-edge solutions.
2. Key Features and Services Comparison
Pricing Structures: A Detailed Analysis
One of the critical factors in choosing a cloud provider is the pricing model. Each of the Big 3 cloud providers has its unique approach to pricing, and understanding these nuances can significantly impact your organization's budget. Here's a brief overview:
- AWS Pricing: AWS follows a pay-as-you-go model, allowing users to pay only for the resources they consume. It offers various pricing options, including On-Demand Instances, Reserved Instances, and Spot Instances. Additionally, AWS provides a free tier with limited resources for new users to explore its services without incurring costs.
- Azure Pricing: Microsoft Azure's pricing structure is similar to AWS, with options for Pay-as-You-Go, Reserved VM Instances, and Spot VMs. Azure also offers an Enterprise Agreement for organizations with long-term commitments. The Azure Hybrid Benefit allows users to apply their existing Windows Server or SQL Server licenses to Azure VMs, potentially reducing costs.
- GCP Pricing: Google Cloud Platform emphasizes simplicity and transparency in its pricing. GCP offers Sustained Use Discounts, which automatically reduce costs as you use resources consistently. It also provides a committed use contract for predictable workloads. Google's Free Tier allows users to explore GCP services with specific usage limits at no cost.
Performance Metrics: Speed, Uptime, and Reliability
When it comes to performance, all three providers strive for high availability, low latency, and robust reliability. However, there are subtle differences:
- AWS Performance: AWS boasts a vast global network with multiple availability zones (AZs) in each region. Its Amazon EC2 instances offer various instance types optimized for different workloads. AWS's Service Level Agreements (SLAs) guarantee uptime for services like Amazon S3 and Amazon RDS.
- Azure Performance: Azure's global presence includes data centers in over 60 regions. Azure VMs come in various sizes, and its Virtual Machine Scale Sets allow easy scaling. Azure's Availability Zones ensure redundancy and fault tolerance. SLAs cover services like Azure Blob Storage and Azure SQL Database.
- GCP Performance: Google's network infrastructure is renowned for speed and reliability. GCP's Compute Engine provides customizable VMs, and its Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) simplifies container orchestration. GCP's Multi-Regional Storage Buckets ensure data durability, and SLAs cover services like Bigtable and Cloud Spanner.
Remember that performance metrics can vary based on your specific workload, geographic location, and the services you choose. It's essential to evaluate your requirements and test performance under realistic conditions.
3. Market Share and Growth Trends
As of 2024, the cloud computing market continues to be dominated by the 'Big 3': AWS, Azure, and GCP. AWS maintains the lead with the largest market share, attributed to its early entry into the cloud space and comprehensive service offerings. Azure follows closely, benefiting from seamless integration with Microsoft's vast array of enterprise software. GCP, while having a smaller market share, is recognized for its deep investment in AI and data analytics, attracting businesses focused on these areas.
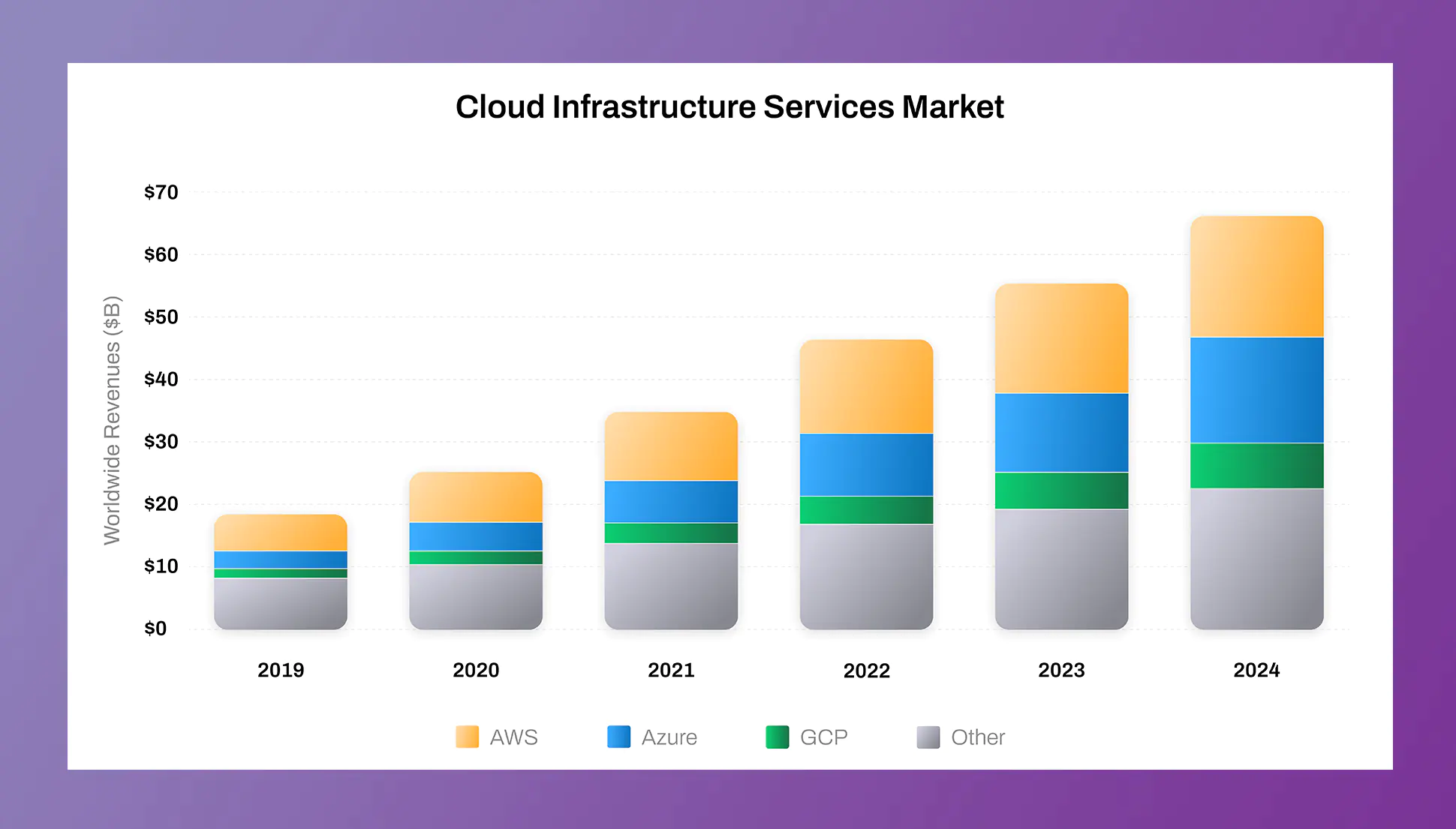
The growth trends indicate a steady increase in adoption as companies continue to embrace digital transformation. The reasons behind their popularity include continuous innovation, global reach, and a strong emphasis on security and compliance, which resonate with the needs of modern businesses.
| Cloud Provider | Market Share (2024) | Growth Trends (2024) |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | 39% | Steady growth |
| Microsoft Azure | 31% | Rapid growth |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | 14% | Consistent growth |
| Others | 16% | Slow growth |
4. GPU on Demand for AI and ML
The advent of AI and ML has necessitated robust computational power, and GPUs have emerged as the linchpin for these demanding tasks. AWS, Azure, and GCP offer on-demand GPU services that cater to the diverse needs of AI and ML projects. AWS's EC2 P3 instances are equipped with NVIDIA Tesla V100 GPUs, designed for heavy machine learning workloads. Azure's N-Series virtual machines provide NVIDIA GPUs that support various AI development environments. Similarly, GCP's AI Platform offers powerful NVIDIA T4 and V100 GPUs, ensuring that users can scale their ML models efficiently. These on-demand GPU services are not just about raw power; they're also about flexibility and scalability, allowing developers to choose the right size and configuration for their project's unique requirements.
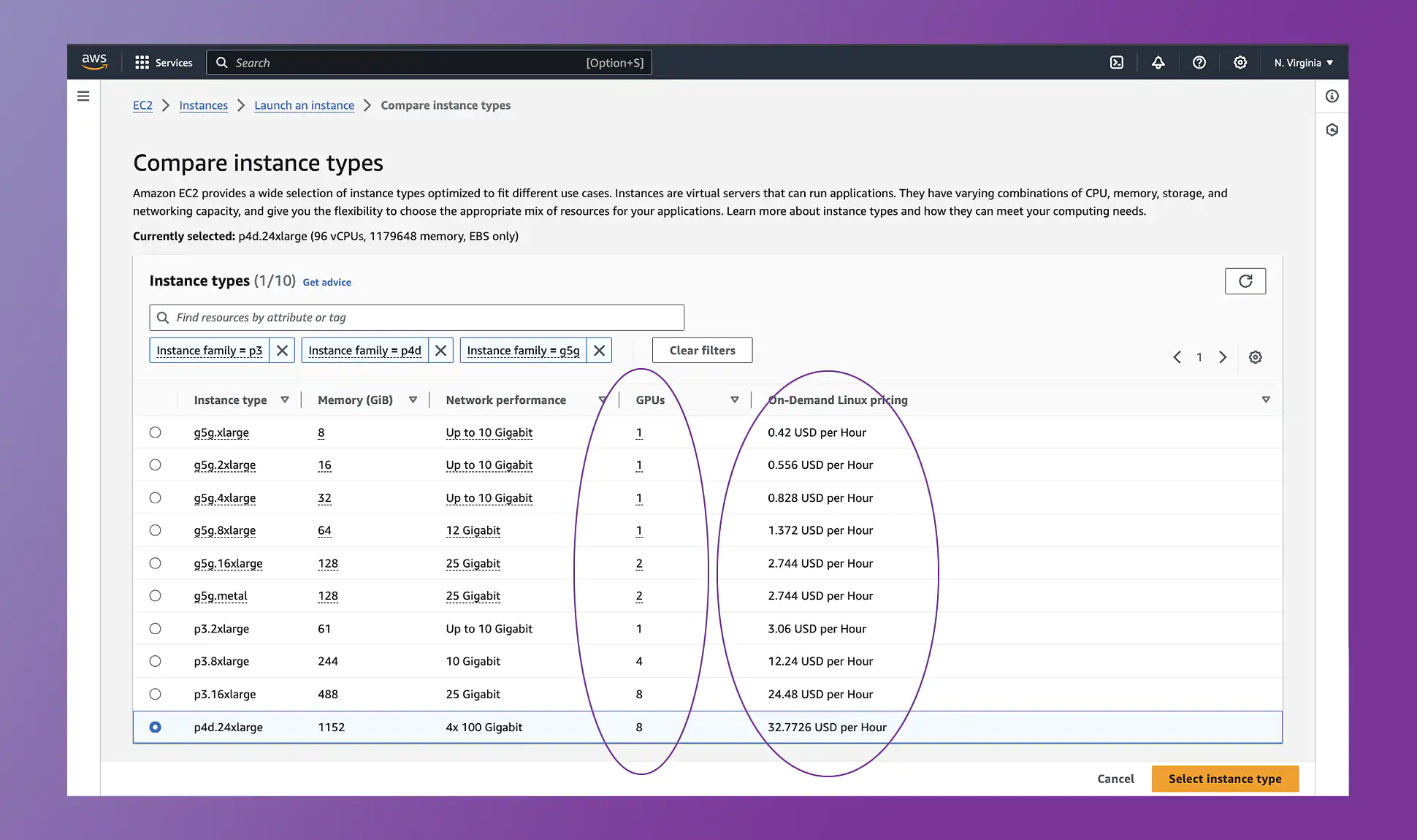
Let's compare the GPU on-demand offerings from the three major cloud providers: AWS, Azure, and GCP. Keep in mind that GPU availability and pricing may vary by region and instance type.
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
- EC2 P3 Instances: These instances offer NVIDIA V100 GPUs with either 16 GB or 32 GB of GPU memory. They are suitable for deep learning, scientific simulations, and other GPU-intensive workloads.
- EC2 P4d Instances: These instances feature NVIDIA A100 GPUs with 40 GB or 80 GB of GPU memory. They excel in AI training, high-performance computing, and data analytics.
Microsoft Azure:
- NCas_T4_v3 Instances: These instances come with NVIDIA T4 GPUs, suitable for AI inference, machine learning, and video transcoding.
- NDv2-series Instances: These instances offer NVIDIA V100 GPUs with 16 GB of GPU memory. They are ideal for deep learning, scientific computing, and data analytics.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- Compute Engine P4 Instances: These instances feature NVIDIA A100 GPUs with 40 GB of GPU memory. They excel in AI/ML training, scientific simulations, and data analytics.
- Compute Engine V100 Instances: These instances come with NVIDIA V100 GPUs (16 GB or 32 GB), suitable for deep learning, HPC, and data processing.
In terms of variety, Azure offers the most GPU options, while AWS and GCP are equivalent at the top end with 8-way V100 and A100 configurations. Pricing varies based on the specific GPU type, memory, and region. Remember to check the latest pricing details directly from the cloud provider's official documentation for accurate information.
5. Security Features and Compliance
In the realm of cloud computing, security is paramount. AWS, Azure, and GCP have all established comprehensive security measures to protect customer data. AWS offers a suite of security services such as AWS Shield for DDoS protection and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to AWS services. Azure boasts of its Azure Security Center, which provides unified security management and advanced threat protection across hybrid cloud workloads. GCP's Security Command Center helps identify and manage security risks in your GCP resources. Moreover, all three providers comply with a broad set of international and industry-specific compliance standards, including GDPR, HIPAA, and FedRAMP, ensuring that businesses can meet their regulatory requirements with ease.
| Threat Category | AWS | Azure | GCP |
| Data Breaches | - Encryption at Rest - Amazon S3 Access Control - AWS IAM | - Azure Disk Encryption - Azure Key Vault - Azure AD | - Customer-Supplied Encryption Keys - Data Loss Prevention API |
| DDoS Attacks | - AWS Shield - Amazon CloudFront | - Azure DDoS Protection - Azure Front Door | - Google Cloud Armor - Global Load Balancer |
| Identity Compromise | - Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) - AWS SSO | - Azure AD Conditional Access - Azure Managed Identities | - Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP) - Context-Aware Access |
| Insider Threats | - AWS CloudTrail - AWS Organizations | - Azure Monitor - Azure Policy | - Google Cloud Audit Logs - VPC Service Controls |
| Compliance Challenges | - AWS Artifact - AWS Config | - Azure Compliance Manager - Azure Blueprints | - Google Cloud Compliance - Google Cloud DLP |
6. Global Infrastructure and Availability Zones
The global infrastructure of AWS, Azure, and GCP is a testament to their reliability and commitment to providing uninterrupted service. AWS has the largest number of data centers, spread across 24 geographic regions and 77 availability zones. Azure's infrastructure spans 60+ regions, more than any other cloud provider, offering greater flexibility and options for data residency. GCP's network, though smaller, is renowned for its high-speed fiber-optic cables that ensure low-latency connections. The strategic placement of these data centers and availability zones minimizes latency, maximizes redundancy, and allows businesses to operate resiliently at a global scale.
7. Case Studies: Successful Deployments
Case studies of successful deployments underscore the capabilities of the Big 3 cloud providers. AWS's collaboration with Netflix is a prime example, where AWS's scalability supports over 200 million subscribers globally. Azure's partnership with eBay showcases its ability to handle over 1 billion listings with ease, demonstrating Azure's robust e-commerce capabilities. GCP's work with Spotify highlights its data analytics prowess, managing over 70 million tracks and 4 billion playlists. These cases illustrate not just the technical proficiency of the cloud providers but also their ability to support businesses in achieving their objectives and driving innovation.
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
- Ryanair: revolutionizes air travel with Amazon Bedrock and Amazon Connect
- Capital One: Saves developer time and reduces costs by going serverless on AWS
- Unilever: Improved time-to-market for consumer goods using AWS's standardized technology.
- Expedia: Utilized AWS for their global travel booking platform, handling millions of transactions daily.
Microsoft Azure:
- NBC Olympics: Used Azure for streaming the Olympic Games, supporting a vast number of viewers.
- 3M: Boosted mobile-app development and gained real-time insight, impacting their customer base.
- HarperCollins: Employed Azure to scale major TV and social media campaigns.
- Mazda: Achieved better data protection and 95% lower costs using Azure hybrid cloud storage.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
- Current: A fintech company that improved app development time by 400% while serving over 175,000 users daily without downtime.
- JencoMart: A global retailer that migrated critical applications to GCP to optimize for capacity and value.
- Big Data Analytics: Leveraged GCP's analytics capabilities to drive informed decision-making across industries.
- EHR Healthcare: Utilized GCP for healthcare data management, enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.
These companies represent a fraction of the enterprises that have successfully harnessed the power of cloud computing to transform their operations and services.
8. Recommendations for Industry Needs
When selecting a cloud provider, it's crucial to consider the unique requirements of your industry. AWS is renowned for its extensive service offerings and robust computing capabilities, making it a strong choice for industries with heavy workloads, such as biotech and logistics. Azure is preferred by many enterprises for its seamless integration with Microsoft products, which can be a significant advantage for organizations that rely on Windows-based applications. GCP shines with its data analytics and machine learning services, which are ideal for industries like retail and media that require advanced data processing and insights.
For instance, healthcare organizations prioritize compliance and data security, and may lean towards Azure for its comprehensive compliance coverage. E-commerce businesses, on the other hand, might benefit from AWS's global reach and scalability to handle fluctuating traffic volumes. Startups and tech companies may find GCP's cutting-edge AI tools and pricing model more aligned with their innovative and cost-conscious approach.
9. Choosing the Right Platform
The decision to choose between AWS, Azure, and GCP should be informed by a thorough evaluation of your business needs. AWS offers the most extensive global infrastructure, which is beneficial for businesses requiring a broad reach. Azure provides deep integration with enterprise software and a strong focus on hybrid cloud, making it ideal for businesses with existing Microsoft investments. GCP offers powerful analytics and machine learning services, which can be advantageous for data-driven businesses.
AWS:
- Pros: Largest service catalog, extensive global network.
- Cons: Can be complex to navigate due to the vast array of offerings.
Azure:
- Pros: Seamless integration with Microsoft services, strong enterprise focus.
- Cons: May require a steeper learning curve for non-Microsoft users.
GCP:
- Pros: Leading-edge AI and data analytics, competitive pricing.
- Cons: Smaller global footprint compared to AWS and Azure.
Ultimately, the right platform is one that aligns with your strategic goals, technical requirements, and budget constraints. It's advisable to conduct a pilot project or consult with a cloud expert to make an informed decision.
10. The Future of Cloud Computing
As we peer into the horizon of cloud computing, several trends emerge, shaping the landscape beyond 2024. Let's explore some of these exciting developments:
- Serverless Computing: The serverless paradigm, where developers focus on code without managing infrastructure, will continue to gain traction. Services like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions allow businesses to execute code in response to events, paying only for actual usage.
- Edge Computing: As IoT devices proliferate, edge computing-processing data closer to the source - will become critical. Cloud providers are expanding their edge services, enabling real-time analytics and low-latency applications.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Organizations increasingly adopt hybrid and multi-cloud architectures. Seamless integration between on-premises data centers and public clouds, along with workload portability, will be essential.
- Quantum Computing: While still in its infancy, quantum computing promises breakthroughs in optimization, cryptography, and scientific simulations. Cloud providers are investing in quantum services, preparing for a quantum-powered future.
- Sustainability and Green Computing: Cloud providers are committed to reducing their environmental impact. Expect innovations in energy-efficient data centers, renewable energy adoption, and carbon-neutral cloud services.
- AI-Driven Automation: AI and machine learning will automate routine tasks, optimize resource allocation, and enhance security. Auto-scaling, anomaly detection, and predictive maintenance will become standard.
- Blockchain Integration: Cloud platforms will integrate blockchain services for secure, transparent, and decentralized applications. Smart contracts, supply chain tracking, and identity management will benefit.
- Containerization and Kubernetes: Containers (e.g., Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes) simplify deployment and management. Expect further advancements in container security and ease of use.
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Stricter regulations (e.g., GDPR) will drive cloud providers to enhance data privacy features. Compliance certifications and robust encryption will be paramount.
- Collaboration with Industry Verticals: Cloud providers will deepen their collaboration with specific industries (e.g., healthcare, finance, manufacturing). Tailored solutions will address unique challenges.
In this dynamic landscape, businesses must stay agile, adapt to emerging technologies, and choose cloud partners wisely. The future of cloud computing is not just about infrastructure - it's about enabling innovation, resilience, and sustainable growth.
Conclusion
The exploration of cloud computing through the lens of the industry's giants - AWS, Azure, and GCP - reveals a landscape rich with innovation, growth, and potential. As businesses continue to navigate the digital transformation, the choice of a cloud provider becomes a pivotal decision that can shape their future success. The "Big 3" have each carved out their niches, offering a range of services that cater to different needs and industry demands.
AWS remains the market leader with its vast array of services and global infrastructure, Azure appeals to enterprises with its deep integration with Microsoft's suite of products, and GCP stands out with its data analytics and machine learning prowess. The case studies of companies like Thorn, Unilever, and Expedia for AWS; NBC Olympics, 3M, and HarperCollins for Azure; and Current, JencoMart, and EHR Healthcare for GCP, demonstrate the transformative power of cloud computing.
In conclusion, the journey to the cloud is unique for every organization. It requires a thoughtful approach, considering not only the technical capabilities but also the strategic alignment with business objectives. The future is cloud-native, and the decisions made today will lay the foundation for tomorrow's success.

